
ROTEM sigma
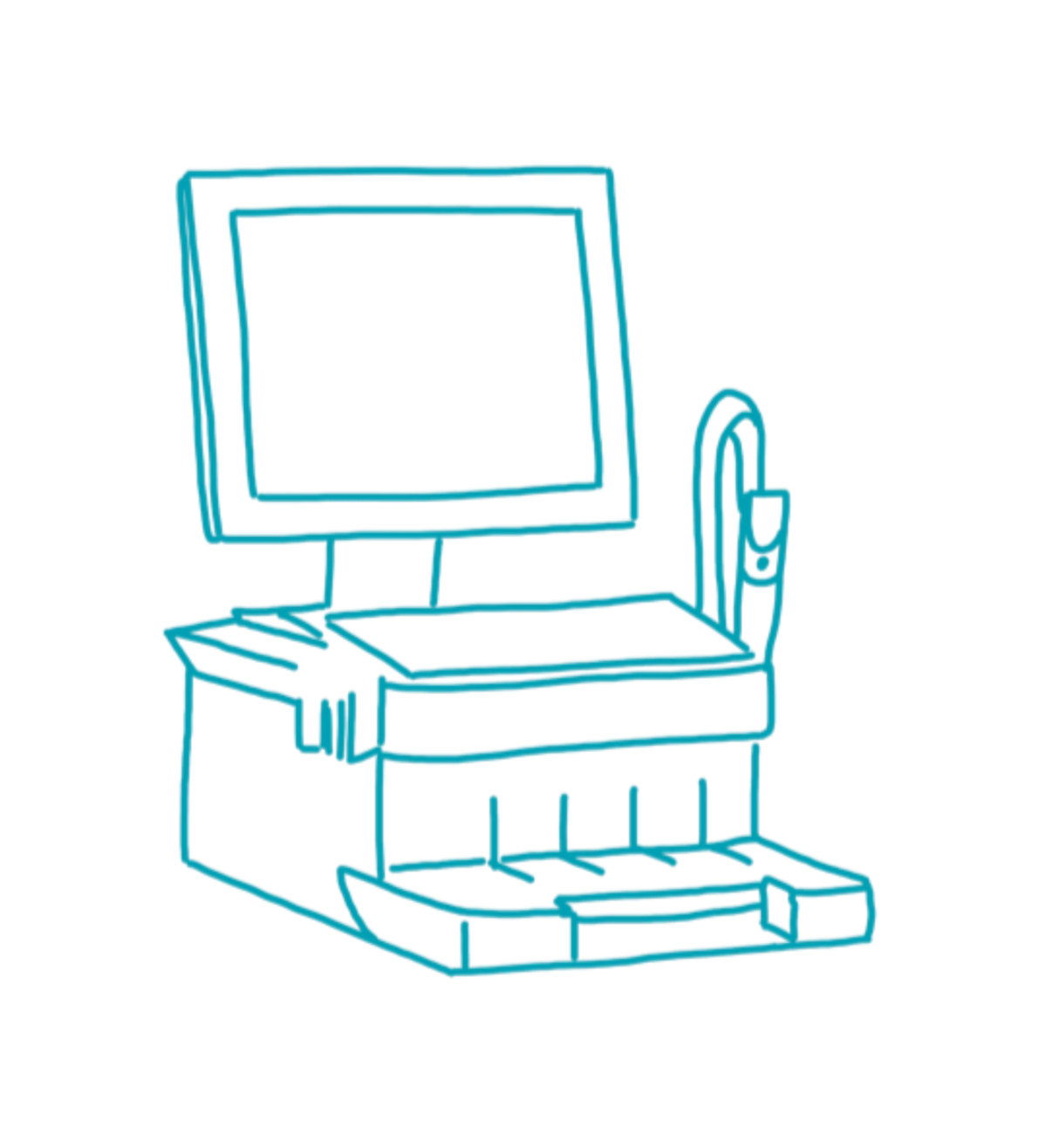
ROTEM sigma ist ein vollautomatisiertes System für die viskoelastische Gerinnungsanalyse am Point-of-Care. Es liefert innerhalb weniger Minuten präzise Informationen über die Gerinnselbildung, -festigkeit und -stabilität aus Vollblut und unterstützt Kliniken bei der schnellen Identifikation von Blutungsursachen. Das System optimiert klinische Entscheidungswege in Herzchirurgie, Trauma, Intensivmedizin und Transplantationsmedizin und trägt zu einem zielgerichteten, evidenzbasierten Blutungsmanagement bei.
ROTEM sigma nutzt eine geschlossene Cartridge-Technologie, die ohne Pipettieren auskommt und die Probe automatisiert aus dem geschlossenen Blutröhrchen einzieht. Über vier parallele Messkanäle analysiert das System die gesamte Gerinnungsdynamik in Echtzeit und stellt alle Ergebnisse in klar strukturierten TEMogrammen dar. Optimierte Aktivatoren sorgen für Testergebnisse in unter zehn Minuten, während Amplituden- und Stabilitätsparameter nach etwa fünfzehn Minuten verfügbar sind. Die integrierte Qualitätskontrolle überwacht fortlaufend das System und sorgt für reproduzierbare, belastbare Messergebnisse. Da alle Reagenzien in den Cartridges bereits enthalten sind und diese bei Raumtemperatur gelagert werden können, lässt sich das System ohne Vorbereitung unmittelbar am Point-of-Care einsetzen.
- Herzchirurgie und kardiovaskuläre Eingriffe
- Traumachirurgie und Schockraumversorgung
- Intensivstation
- Lebertransplantationen
- Geburtshilfe bei postpartalen Blutungen
- Operative Settings mit hohem Risiko für akute Koagulopathien
- Schnelle Identifikation von Fibrinogenmangel, Thrombozytopenie oder Hyperfibrinolyse
- Unterstützung bei Transfusionsentscheidungen nach PBM-konformen Algorithmen
- Hämostase-Monitoring während Operationen mit hohem Blutverlust
- Evaluation der Gerinnung unter Heparin-Einfluss, z. B. bei Herz-Lungen-Maschine
- Überwachung der Gerinnselstabilität bei kritisch kranken Patienten
- Echtzeit-basierte Therapieanpassung in massiven Blutungssituationen
- Entscheidungsrelevante Ergebnisse in weniger als zehn Minuten
- Vollautomatisierter Workflow ohne Pipettieren oder Probenvorbereitung
- Vier simultane Testkanäle für eine schnelle differentialdiagnostische Bewertung
- TEMogramme mit klaren Referenzbereichen erleichtern die klinische Interpretation
- Integrierte Qualitätskontrollen erhöhen Prozesssicherheit und Reproduzierbarkeit
- Cartridges sind bei Raumtemperatur lagerbar und sofort einsetzbar
- Optimale Integration in PBM-Programme zur Reduktion unnötiger Transfusionen
- Echtzeit-Remotezugriff auf TEMogramme über klinische Datenmanagementsysteme
Dieses System bietet einen vollständig automatisierten Workflow. Der Verzicht auf Pipettierung reduziert Fehler und Schulungsaufwand, während halbautomatische Lösungen mehr manuelle Schritte erfordern. Vier parallele Messkanäle liefern schneller alle relevanten Parameter, Systeme mit weniger Kanälen bremsen in akuten Situationen die Entscheidungsfindung. Die geschlossene Kartuschentechnik erleichtert Handhabung und Standardisierung am Einsatzort. Andere Geräte benötigen teils zusätzliche Vorbereitung, was Abläufe verzögert. Auch die IT-Anbindung ist breiter aufgestellt: Wettbewerber bieten teilweise nur eingeschränkte Schnittstellen oder arbeiten mit externer Middleware, wodurch Informationen später verfügbar sind.
Testübersicht (2)
Cartridge Complete
Cartrdige Complete +Hep
Cartridge Complete
Cartrdige Complete +Hep
Studien & Produktdokumente
Evaluation of fibrinogen concentrate for hemostasis during thoracic aortic surgery (complete republication).
Automated Thromboelastometry for Semiquantitative Assessment of High Heparin Concentrations: A Feasibility Study in Healthy Volunteers.
What the Sigma? Exploring the Change From Single to Dual Anti-Platelet ROTEM on the FIBTEM to Clauss Fibrinogen Relationship in Neurotrauma.
Point-of-care visco-elastic testing for postpartum haemorrhage: A narrative review.
Effects of pneumatic tube systems on viscoelastic coagulation tests in septic patients and healthy individuals: protocol of the randomized controlled VETaPT-trial.
Case-control study of clotting differences using ROTEM testing in pregnant patients with early vaginal bleeding.
Relationship between the dual platelet-inhibited ROTEM® Sigma FIBTEM assay and Clauss fibrinogen during postpartum haemorrhage.
Can rotational thromboelastometry rapidly identify theragnostic targets in isolated traumatic brain injury?
Assessing coagulopathy and endothelial dysfunction in pediatric venous malformation: A thromboelastometry and syndecan-1 study.
Hemostatic Profiles of Patients Who Underwent Transcatheter Versus Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement Versus Percutaneous Coronary Intervention.
Variability in viscoelastic haemostatic assay in major haemorrhage protocols: A unified approach or mixed signals?
Comparison of 2 thromboelastography methods using patient and control samples.
Thromboelastometry and two activated clotting tests in detecting residual heparin after protamine in cardiac surgical patients: A prospective cohort study.
Comparison of ROTEM® Delta and ROTEM® Sigma transfusion algorithm performance in thoracic aortic surgery: a single-centre prospective observational cohort study.
Fibrinogen levels in severe trauma: A preliminary comparison of Clauss Fibrinogen, ROTEM Sigma, ROTEM Delta and TEG 6s assays from the FEISTY pilot randomised clinical trial.
Viscoelastic testing: Critical appraisal of new methodologies and current literature.
Point-of-Care Viscoelastic Hemostatic Assays in Cardiac Surgery Patients: Comparison of Thromboelastography 6S, Thromboelastometry Sigma, and Quantra.
Are Viscoelastometric Assays of Old Generation Ready for Disposal? Comment on Volod et al. Viscoelastic Hemostatic Assays: A Primer on Legacy and New Generation Devices. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 860.
A comparison of the ClotPro system with rotational thromboelastometry in cardiac surgery: a prospective observational study.
Comparison of coagulation monitoring using ROTEM and Sonoclot devices in cardiac surgery: a single-center prospective observational study.
Pre-operative reference ranges for ROTEM® sigma in patients undergoing cardiac surgery: a secondary analysis of two prospective trial cohorts.
An audit of the diagnostic accuracy of the ROTEM®sigma for the identification of hypofibrinogenaemia in cardiac surgical patients.
The influence of FIBTEM and EXTEM clotting times on the diagnostic accuracy of ROTEM® sigma identification of hypofibrinogenaemia during cardiac surgery.
Prediction of platelet counts with ROTEM-sigma in cardiac surgery.
The sensitivity and specificity of rotational thromboelastometry (ROTEM) to detect coagulopathy during moderate and severe postpartum haemorrhage: a prospective observational study.
Characterization of 2 Different Prothrombin Complex Concentrates by Different Hemostatic Assays in an In Vitro Hemodilution Model.
Diagnostic performance of thromboelastometry in trauma-induced coagulopathy: a comparison between two level I trauma centres using two different devices.
Comparison of ROTEM Sigma to Standard Laboratory Tests and Development of an Algorithm for the Management of Coagulopathic Bleeding in a Tertiary Center.
ROTEM® sigma reference range validity.